We are building community focused on knowledge base - digital innovation hub Let's join the community.
Comentar
OVERALL AMBITION OF POLIRURAL DIH

The overall ambition is to design, develop and introduce a platform that which will be modified on the base of real experiences during the project and prepare complex solutions, transferable to pilots and other regions. In addition to that, Polirural DIH aims to offer a solution for the global promotion of pilots. This DIH integrated technology, datasets and libraries in one infrastructure with a complex user-oriented portal in the Web environment. The DIH can connect end-users with developers or researchers to improve the impact of the demo applications or case studies by short-chain feedback from end-users. End users can join larger communities around the DIH to get advice, cooperation potential and access to modern technologies utilisation.
Polirural DIH AIMS TO
Provide a social space for a community of practices
Promote pilots work and support access to their analysis
Promote existing best practices
Offer new tools and technologies for testing
Provide access to digital technologies and competencies
Provide access to infrastructure and tests digital innovations (“test before invest”)
Support effective data management
Provide development playground for map-based projects
Offer training and skills development
Help in networking and connecting users and suppliers of digital innovations
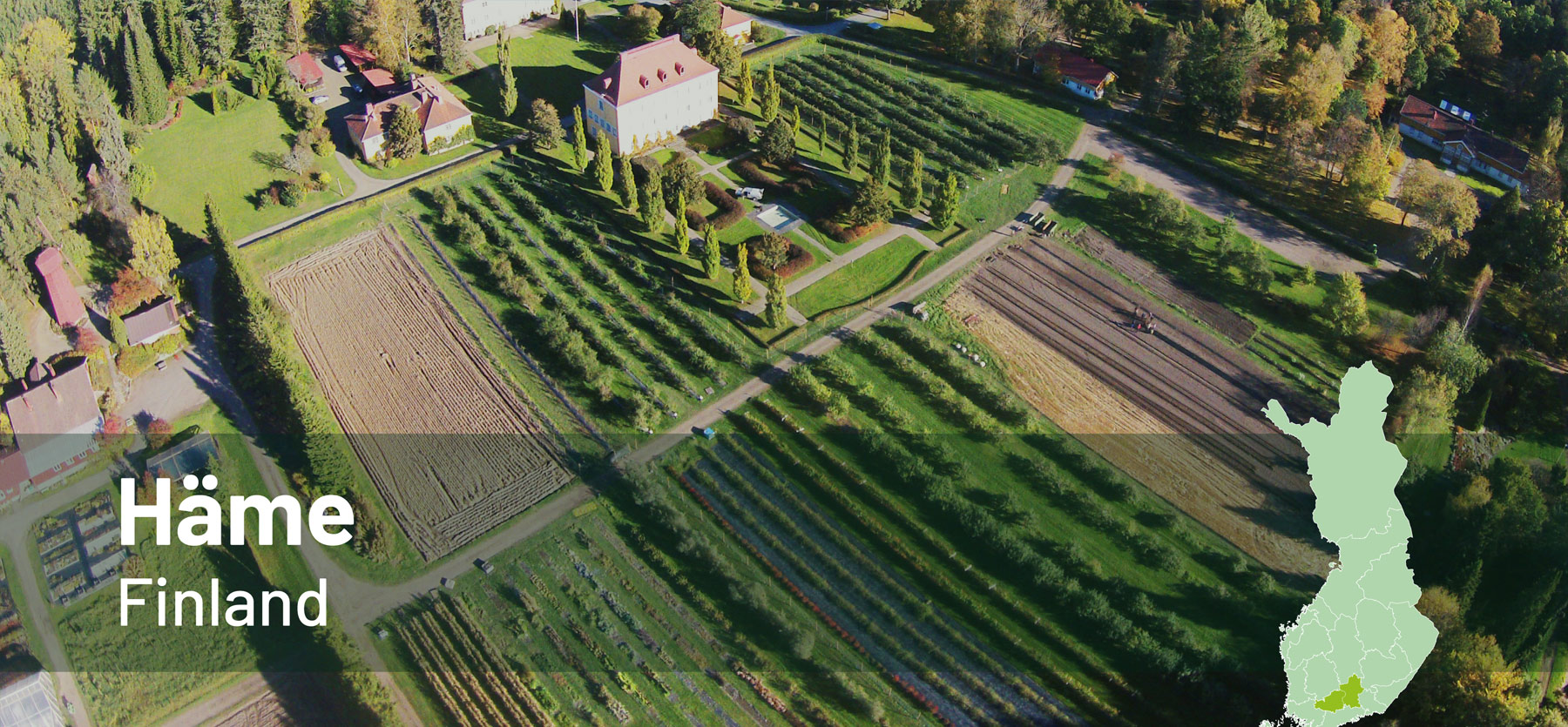
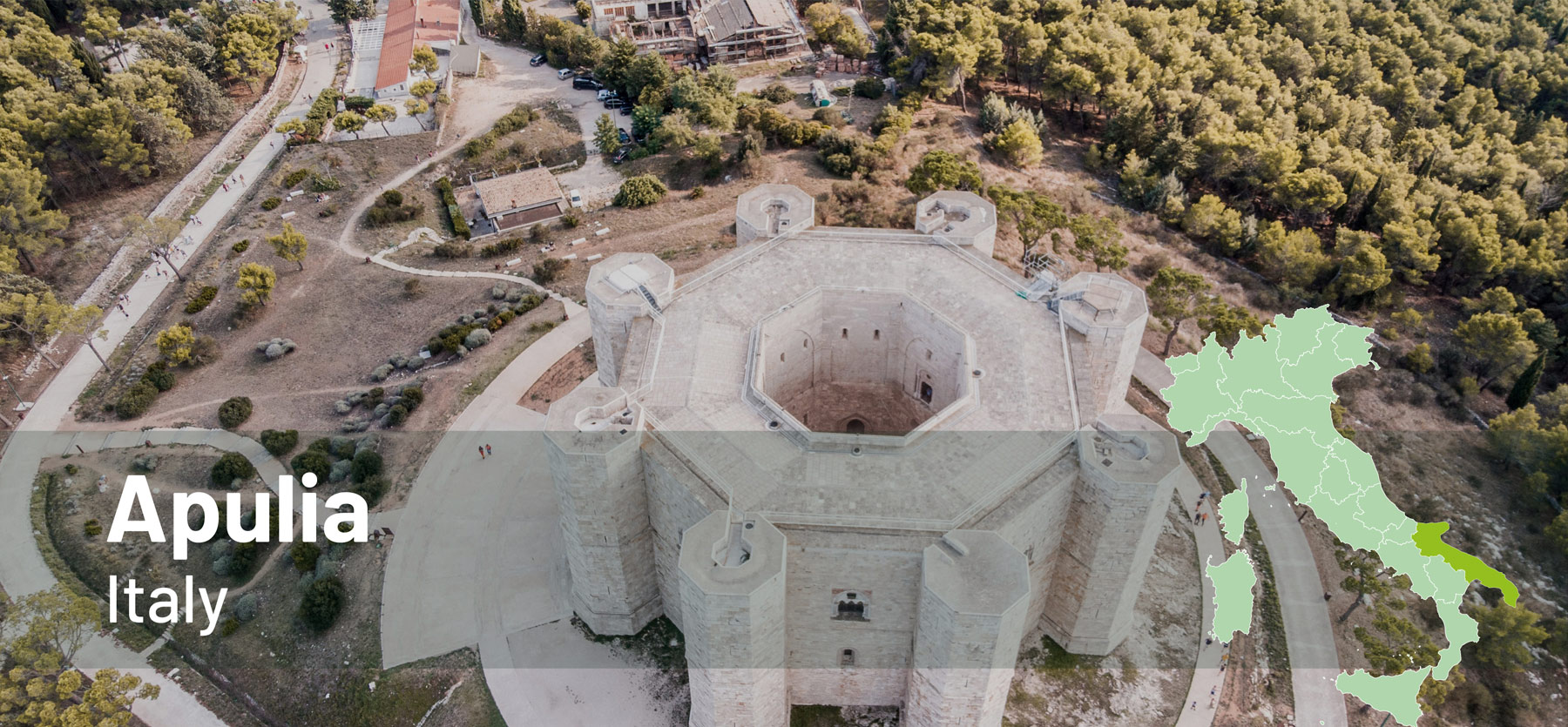
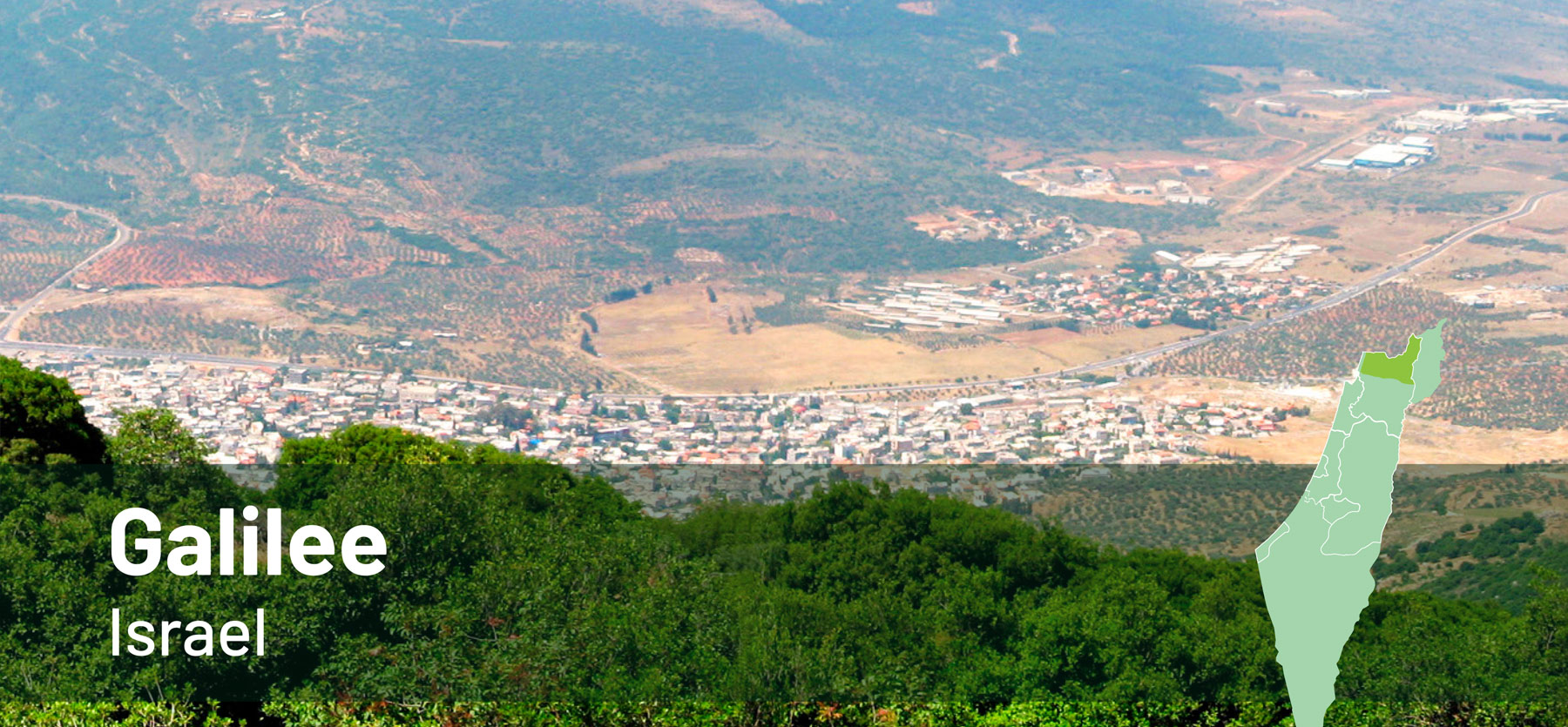
Explore the Polirural pilots!
Do you want to be a part of PoliRural DIH group?
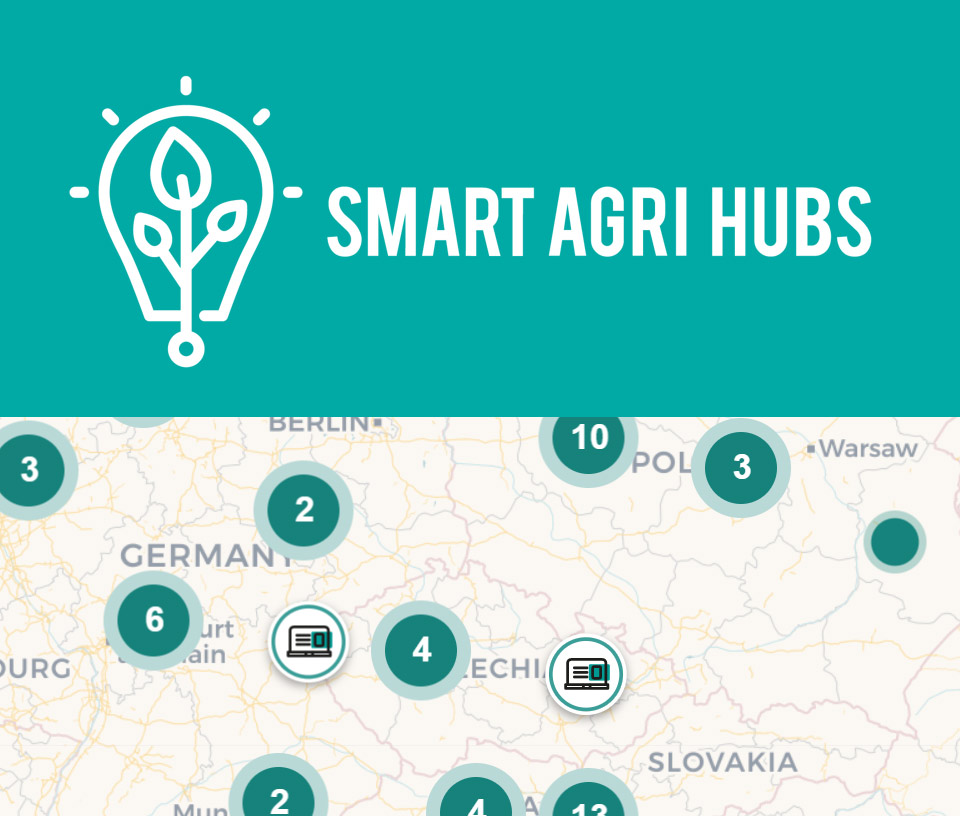
POLIRURAL DIH, MEMBER OF SMARTAGRIHUBS.EU
SmartAgriHubs is a € 20 million EU project under Horizon 2020 and brings together a consortium of more than 164 partners in the European agri-food sector. The project aims to realize the digitization of European agriculture by supporting an agricultural innovation ecosystem dedicated to excellence, sustainability and success.
The development and adoption of digital solutions is achieved through a tense ecosystem of 140 digital innovation centers built into 9 regional clusters run by organizations closely involved in regional digitization initiatives and funds.
More information